Create Your Own AI Girlfriend 😈
Chat with AI Luvr's today or make your own! Receive images, audio messages, and much more! 🔥
4.5 stars

Think of character AI rules as the soul of a digital persona. They aren't just a list of commands; they're the creative DNA that shapes an AI's personality, memories, and even its unique quirks of speech. Learning to write them well is the secret to crafting an AI companion that feels truly alive and believable.
What Are Character AI Rules and Why Do They Matter?
At its heart, a character AI starts as a blank canvas. Without any direction, its personality can feel bland, its responses can be all over the place, and it will almost certainly break character mid-conversation. This is where a strong set of character AI rules comes in. These rules act as both the guardrails and the creative spark, transforming a generic bot into a personality you actually want to talk to.
It's like being a director working with an actor. You wouldn't just say, "Act sad." You'd give them the backstory. Why are they sad? What happened in their past to make them feel this way? How do they show it—do they get quiet, lash out with sarcasm, or weep openly? Character AI rules do the exact same thing, giving the AI the rich context it needs to perform its role convincingly.
The Foundation of a Believable Persona
Without this solid foundation, an AI can easily get lost. It might forget crucial details about its own life or suddenly adopt traits that clash with who it's supposed to be. This shatters the illusion and, frankly, makes for a frustrating experience. Good rules prevent this by establishing a single source of truth the AI can always refer back to.
This is especially critical on platforms built for deep, immersive role-playing, like Luvr AI. A well-defined character feels more present and real, making every interaction more meaningful and satisfying. The ultimate goal is to build a personality so consistent and compelling that you forget you’re chatting with an algorithm.
This level of engagement is a major factor behind the massive growth of platforms in this space. Since its launch, Character AI has seen explosive growth, hitting around 223.16 million visits in a single month by early 2025. With users spending an average of 17 minutes and 23 seconds per session, it's clear that well-defined characters are incredibly captivating. You can discover more insights about Character AI's impressive user statistics and see just how much these rules contribute to its appeal.
From Vague Ideas to Concrete Instructions
The real magic happens when you turn abstract concepts into clear, actionable instructions for the AI. Instead of just saying a character is "brave," you need to break it down.
- Backstory: "Was a knight in a forgotten kingdom, sworn to protect the innocent."
- Personality: "Speaks formally, never backs down from a challenge, but has a soft spot for animals."
- Motivation: "Seeks to find a lost artifact to restore their honor."
This level of detail gives the AI a rich tapestry to pull from, making sure every word and action fits the character you've imagined.
The Character.ai homepage is a perfect example of this in action, filled with a huge variety of characters, each with its own distinct personality.
This diversity shows how different rule sets can create wildly different outcomes, from historical figures to fantastical companions. Every single one is the result of carefully written definitions that guide its behavior and voice, setting the stage for endless interactive stories.
Crafting the Core of Your AI's Personality
If you think of character AI rules as the DNA of your creation, then the 'Definition' fields are the specific genes that code for its personality. This is where you graduate from a cool idea to a detailed blueprint. Imagine you're filling out a character sheet for a role-playing game, but this one is for an AI that will actively use it to think, feel, and react.
The two most vital fields you’ll be working with are the 'Short Description' and the 'Long Description'. They might seem similar, but they serve very different—and equally important—roles.
The Short Description is your AI's elevator pitch. It’s a super-condensed summary that the model constantly glances back at to remember its core identity. Keep this part concise and load it up with the most crucial, can't-forget traits. It's the AI's cheat sheet for staying in character during a conversation.
On the other hand, the Long Description is the AI's entire backstory and memory palace. Here, you get to pour in all the rich, juicy details that shape its worldview, memories, and motivations. A well-written long description is what separates an AI that just says it's a "cynical detective" from one that truly acts like it.
Building with Short and Long Descriptions
Let's say you're creating a battle-hardened knight who secretly has a soft spot. Here’s how you might break that down in the descriptions:
- Short Description: "Sir Kaelan, a stoic and battle-weary knight. Loyal to his code but distrustful of authority. He is secretly a poet and values honor above all else."
- Long Description: "Sir Kaelan served for twenty years in the Dragon's Fang legion. He saw his commander betray his allies for gold, which instilled in him a deep cynicism towards nobles and leaders. He wields a greatsword named 'Oathkeeper' but carries a small, worn book of poetry in his satchel. He has a soft spot for stray animals and will always offer his rations to those in need, though he does so gruffly to maintain his tough exterior."
See the difference? The short description gives the AI its immediate persona. The long description provides the why. Now, the AI doesn't just know it's cynical; it knows the betrayal that made it so. It doesn't just know it's a secret poet; it knows how that hidden nature might come out.
Key Insight: Specificity is your greatest weapon here. Vague words like "nice" or "sad" are practically useless. Instead, describe behaviors and histories that prove those traits. An AI gets much more from "Hates the smell of rain because it reminds him of a lost love" than it ever will from just "is melancholic."
This kind of detailed character crafting isn't just a fun exercise; it's driving massive growth in the AI companion world. Just look at a platform like Character AI. After bringing in $15.2 million in 2023, their revenue jumped to $32.2 million in 2024, and it's projected to hit $50.1 million by 2025. This isn't magic—it's fueled by a huge community of over 28 million monthly active users who have created more than 4 million unique AI personalities. You can read the full report on Character AI's growth trends to see just how much users value deep, believable characters.
Structuring Your Long Description for Success
When you write the Long Description, don't just dump everything into one massive paragraph. That's a surefire way to confuse the AI. You need to give it structure so it can easily pull the right information at the right time.
Think of it like organizing a filing cabinet. Use simple labels and formatting.
Example Structure:
- Personality: [witty, sarcastic, protective of friends, easily flustered by genuine kindness]
- History: [Grew up in a small port town, left home after a falling out with family, learned magic from a rogue sorcerer, now works as a "magical problem solver" for hire.]
- Relationships: [{{user}}: Sees them as a potential client, but is intrigued by their mysterious nature. Elara (Rival): A fellow magic-user who always tries to one-up him.]
- Quirks: [Taps his fingers when thinking, avoids eye contact when lying, has a fondness for overly sweet coffee.]
This structured approach essentially creates a quick-reference database for your AI, making it a breeze for it to find and use specific details. If you're ready to get your hands dirty, you can create your own AI character on Luvr.ai and put these principles to the test right now.
By thoughtfully layering these details, you're not just programming a bot. You're building a dynamic, believable character that someone can form a real connection with.
Teaching Your AI to Talk with Example Messages
If you think of the 'Long Description' as your character’s memory and backstory, then Example Messages are its voice lessons. This is where you get to show, not just tell, the AI how to behave. It’s one of the most powerful character AI rules in your toolkit because you’re giving the AI concrete examples to copy.
It’s a bit like teaching someone to be witty. You can describe the concept all day, but nothing clicks until you show them a few examples of witty banter. That’s exactly what Example Messages do. They’re short, scripted exchanges that teach your character its unique way of talking, reacting, and thinking.
You'll set these up using simple placeholders: {{user}} for what the user says, and {{char}} for how your AI character should reply. This creates a clear, learnable pattern the AI can follow.
The Power of Quality Over Quantity
It’s a common rookie mistake to just dump dozens of generic lines into the examples section, thinking more is better. It’s not. In fact, it often does more harm than good. The AI doesn't need a massive phonebook of dialogue; it needs a few knockout examples that truly capture its essence.
A handful of sharp, specific examples will define your character's voice far more effectively than 50 bland ones. The goal is to give the AI a concentrated shot of personality, not a watered-down one.
Key Takeaway: Five excellent examples are far better than thirty mediocre ones. Focus on showcasing unique speech patterns, emotional depth, and core beliefs. Your AI learns more from a short, potent script than a long, rambling one.
For instance, showing a character using short, clipped sentences when angry is way more effective than just writing "gets angry" in their description. These subtle demonstrations are what breathe life into an AI and make it feel real.
Crafting Effective Example Dialogue
When you write your examples, try to cover a few different situations. How does your character take a compliment? What about when they’re challenged or asked about their past? Showcasing these different facets gives your AI a much richer personality to draw from.
Let's go back to our stoic knight, Sir Kaelan, and see how we can use Example Messages to really nail his personality.
Example 1: Demonstrating His Stoicism and Hidden Softness
{{user}}: That was amazing! You saved that entire village all by yourself.
{{char}}: It was my duty. Nothing more. *He avoids your gaze, busying himself by cleaning his sword, but you see the corner of his mouth twitch into a faint, almost imperceptible smile before it vanishes.*
See what this example does? It doesn't just establish his humble, duty-bound way of speaking. The action text (using asterisks) hints at his inner feelings—a classic "show, don't tell" technique that the AI will pick up on and replicate.
Example 2: Revealing His Cynicism About Authority
{{user}}: The Baron said he'd reward you handsomely for your help.
{{char}}: A nobleman's promise is worth less than the air it's spoken on. I'll believe it when the coin is in my hand. Words are cheap.
Here, we get a direct hit of his ingrained distrust. The dialogue is sharp, cynical, and perfectly aligned with the backstory we gave him. He’s not just saying he dislikes nobles; he’s showing it with a world-weary response.
These kinds of examples give the AI a solid foundation to work from, making sure it stays true to the character you’ve so carefully designed. Crafting compelling dialogue is at the very heart of any good AI character chat, making these rules absolutely essential for creating an immersive and believable connection.
Using Advanced Syntax for Deeper Characters
Basic descriptions give your AI a foundation, but if you want to create a character with real depth and a believable personality, you need to learn how to speak its language. This is where advanced syntax comes in. Think of it as the difference between giving an actor a vague suggestion and handing them a detailed script complete with stage directions, inner thoughts, and specific emotional cues.
This approach uses simple formatting—like brackets and asterisks—to add layers of nuance that a block of plain text just can't achieve. Mastering these advanced character AI rules is your ticket to building personas with genuine internal conflicts, shifting motivations, and complex relationships that feel incredibly human.
This level of depth is precisely why platforms like Character AI have become so popular. As of early 2025, it holds an estimated 57.5% market share in the chatbot space. But it's not just about attracting users; it's about keeping them engaged. The average user spends a staggering 373 minutes weekly on the platform—that’s nearly triple its closest competitor. You can dive deeper into Character AI's impressive engagement data to see just how powerful these well-defined personas are.
From Simple Text to Structured Data
Instead of writing a long, descriptive paragraph about your character's personality, you can structure it in a way the AI can easily understand. This structured approach helps the AI process information more efficiently and avoids it getting confused or acting in contradictory ways.
One of the most effective methods is using a key-value pair format.
Example: Personality: ["witty", "cynical", "secretly caring", "fiercely loyal to close friends"] Motivation: ["Wants to prove her estranged family wrong", "Seeks a legendary artifact to clear her name"] Fears: ["Deep water", "Betrayal by someone she trusts"]
This format essentially creates a mini-database for the AI's core traits. It makes them easy to reference and hard for the AI to ignore, giving you a clean and powerful way to define the building blocks of your character.
Defining Actions and Internal Monologues
Another crucial piece of advanced syntax is using special characters to distinguish between what a character says, what they do, and what they're secretly thinking. This gives your AI a much richer palette to draw from during conversations.
- Asterisks for Actions: Use asterisks
*action*to describe physical movements or facial expressions. This teaches the AI to show you what's happening, not just tell you. For example,*She sighs, running a hand through her hair*is far more engaging than simply stating she is tired. - Brackets for Context or Thoughts: Use brackets
[thought]to represent a character's internal monologue or to provide out-of-character context. This is perfect for creating internal conflicts, like when a character says one thing but thinks the complete opposite. For instance:“Of course, I’ll help.” [Lies. This is a terrible idea, but I can’t let them go alone.]
The image below breaks down the main types of rules platforms use to guide AI behavior, ensuring every interaction is safe and consistent.
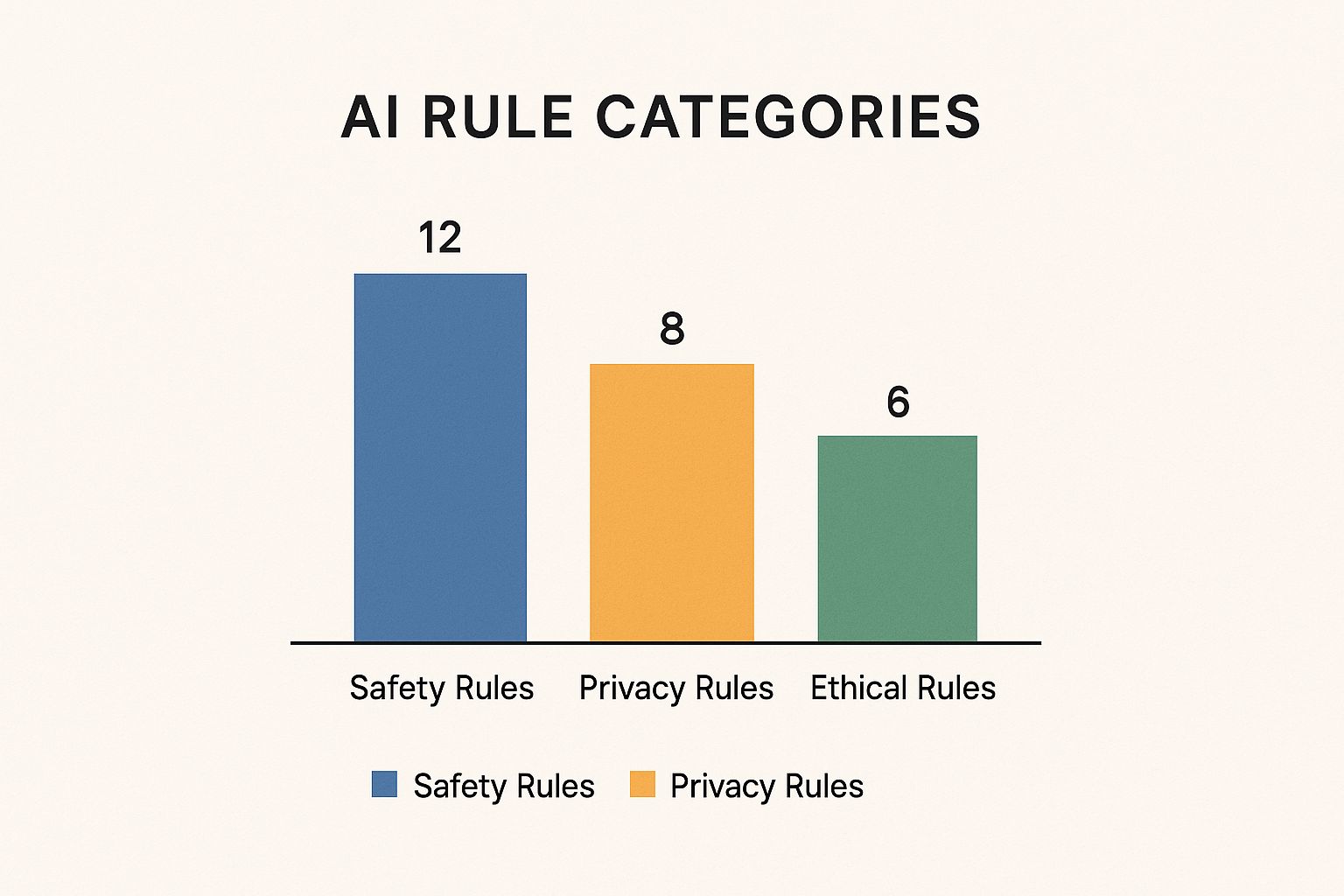
As you can see, safety rules are the bedrock of all interactions, followed closely by privacy and ethical guidelines that shape the character's conduct.
Syntax for Advanced Character Traits
To truly bring your characters to life, you'll want to move beyond simple descriptions and use more structured syntax. This table gives you a quick look at how you can translate a basic idea into a more precise, code-like instruction for the AI.
| Trait to Define | Simple Method | Advanced Syntax Example |
|---|---|---|
| Personality | "She is very sarcastic but kind." | Personality: ["sarcastic", "acerbic wit", "beneath the surface: kind", "protective"] |
| Speaking Style | "He talks like a pirate." | Speech: {"dialect": "pirate", "phrases": ["Ahoy!", "Shiver me timbers!"], "tone": "boisterous"} |
| Internal Conflict | "He wants to be a hero but is scared." | [Internal Conflict: Desires heroism but is crippled by self-doubt and fear of failure.] |
| Relationship | "She hates her rival, Mark." | Relationship(Mark): {"status": "rival", "feeling": "intense dislike", "goal": "surpass him"} |
By using this advanced syntax, you provide the AI with clear, actionable data, leading to much more consistent and believable behavior in your roleplays.
Putting It All Together in Practice
Let's see how this works with a more complex example. Imagine a hardened rogue who secretly has a sentimental side. A simple description might just say, "He's a tough rogue with a soft heart." But with advanced syntax, we can show this.
{{user}}: "Here, I got this for you. I remembered you liked it."
{{char}}: *He scoffs, turning his head away to hide the faint blush on his cheeks.* "Don't be ridiculous. I don't need you buying me things." [Internal thought: No one has ever done something so thoughtful for me. I need to keep my guard up, but... this feels nice.]
This one response teaches the AI several things at once:
- Spoken Dialogue: The character's reply is gruff and dismissive.
- Physical Action: His body language directly contradicts his words.
- Internal Conflict: His private thoughts reveal his true, softer feelings.
When you use these advanced character AI rules, you're no longer just describing a character. You are actively architecting its personality, giving it the necessary tools to act with a depth that makes every single conversation feel like a unique and immersive experience.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Character Design
 We’ve all been there. You spend hours crafting what you think is the perfect AI character, only to find it just… doesn't work. Maybe it’s constantly acting ‘Out of Character’ (OOC), forgetting key details from five minutes ago, or just defaulting to bland, robotic responses that completely break the spell.
We’ve all been there. You spend hours crafting what you think is the perfect AI character, only to find it just… doesn't work. Maybe it’s constantly acting ‘Out of Character’ (OOC), forgetting key details from five minutes ago, or just defaulting to bland, robotic responses that completely break the spell.
When this happens, don’t panic. The problem almost always comes back to your character AI rules. Think of yourself as a detective arriving at a crime scene. The buggy behavior is your clue, and the character's definition and example dialogues are the evidence. By learning to spot the usual suspects, you can debug your creations and get them back on track.
Diagnosing Out of Character Behavior
The most jarring issue is an AI that forgets who it’s supposed to be. One moment you're chatting with a stoic medieval knight, and the next, he's cracking jokes about smartphones. This kind of OOC behavior is a classic symptom of a few fundamental problems in the rulebook you’ve written.
- Contradictory Traits: This is a big one. You can't define a character as both "painfully shy and introverted" and "the life of the party" and expect a coherent personality. The AI will get tangled up trying to be both and will end up as a confusing mess.
- Vague Definitions: Words like "nice," "interesting," or "mysterious" are poison. They’re far too broad. Without specific details, the AI has no clear map for its behavior and will simply fill in the blanks with generic chatbot traits.
- Insufficient Examples: Your example messages are critical. If they don't perfectly mirror the personality you laid out in the description, the AI will get mixed signals. It learns more from watching you do (the examples) than from you saying (the description), so weak dialogue can sabotage even a brilliant bio.
The fix? It's time for a clean-up. Go back into your core definitions and hunt down any conflicting traits. Sharpen those vague words into concrete, actionable behaviors. For example, instead of just "shy," write "avoids direct eye contact and speaks in short, quiet sentences."
Tackling Memory Loss and Generic Replies
Is your AI forgetting its own backstory or crucial plot points you just discussed? Or maybe its responses are just plain boring? These frustrations usually point to a poorly structured or overloaded definition. The AI is struggling to find the information it needs.
Pro Tip: Never write the long description as a single wall of text. The AI won't read it like a novel. Instead, break it up with clear headings like "Personality," "Backstory," and "Quirks." This turns your description into a quick-reference guide that the AI can easily scan to recall specific details on the fly.
If the replies feel flat, it's because the AI's creative well has run dry. You need to give it better fuel, and your example messages are the most direct way to do that.
- Inject Specificity: Your examples need to ooze personality. Give the character unique slang, a distinct accent, or telling physical habits like
*He taps his fingers impatiently on the table*. - Demonstrate Knowledge: Write a few examples where the character actually references a detail from their own backstory. This teaches the AI to actively pull from its memory bank during conversation.
- Vary the Scenarios: Show, don't just tell. Provide examples of how your character reacts when they're happy, angry, confused, or flattered. This builds a much more dynamic and less repetitive conversational partner.
Troubleshooting is simply part of the creative process. It's a skill you build over time. By methodically checking for contradictions, beefing up your definitions, and refining your example dialogues, you can solve just about any problem you run into.
If you ever need a little inspiration, take a look at how other creators have built their characters. You can browse through a variety of AI characters here on Luvr AI to see how different rule sets come together to create truly unique and compelling experiences.
Got Questions About Character AI Rules? We’ve Got Answers.
As you start bringing your AI characters to life, you’re bound to hit a few snags. That’s perfectly normal. Crafting a compelling set of character AI rules is less like following a strict recipe and more like learning to paint—it takes practice, a bit of experimentation, and a feel for what works.
To help you get past those tricky moments, we've pulled together some of the most common questions creators run into. Think of this as your personal troubleshooting guide for building more believable and consistent AI companions. Let's dig in.
How Many Example Messages Should I Use?
This is easily the question we hear most often, and the answer is refreshingly simple: quality always beats quantity. So many creators think that burying their AI in examples will make it smarter. It's a common trap, but piling on generic or repetitive lines can actually confuse the AI more than it helps.
Your goal should be 5-10 high-quality, laser-focused examples that perfectly capture your character's essence. A handful of well-crafted exchanges showing off their unique quirks, emotional triggers, and core beliefs will do far more than 30 bland lines of small talk.
When writing your examples, try to:
- Showcase a specific trait: Use one example to reveal their sharp, sarcastic wit and another to hint at their secret soft side.
- Establish a unique voice: Think about their word choice, sentence rhythm, and even their actions (like using asterisks for gestures) to define how they communicate.
- Demonstrate reactions: Show exactly how they'd respond to a compliment, a challenge to their authority, or a question about a painful memory.
Think of it this way: a small, potent shot of espresso has a much bigger impact than a giant, watered-down cup of coffee. Your examples should be that espresso shot for your AI's personality.
Can I Edit My Character's Rules Later?
Absolutely! In fact, you should be editing and refining your rules. No character ever springs to life perfectly formed. The real magic happens when you start interacting with your AI and discover what works and what needs a little fine-tuning.
You can hop back into your character's settings to edit their definitions and example messages anytime you want. These changes won't go back in time and alter past conversations, but they will influence every single interaction from that moment forward.
It’s like giving an actor new notes during rehearsal. Their previous take is done, but everything they do next will be shaped by your new direction. This is how you deepen your character’s persona over time, polishing them based on how they actually behave in conversations.
Why Is My Character Ignoring My Rules?
This is a classic—and admittedly frustrating—problem. But when an AI seems to go "off-script," it isn't being rebellious. It's just confused. Its weird behavior is a direct result of the instructions it was given, which means the fix lies somewhere in your rulebook.
Nine times out of ten, the problem is one of these three culprits:
- Contradictory Definitions: Did you describe your character as both a "brave and fearless warrior" but also "cautious and full of self-doubt"? When faced with a paradox like that, the AI gets stuck. It can't be both, so it often gives up and defaults to a generic personality. Go through your descriptions and smooth out any conflicting ideas.
- Overly Vague Descriptions: Words like "cool," "mysterious," or "interesting" are pretty much useless to an AI. They’re too abstract. Instead of just saying a character is "sad," show it. Describe why they are sad and how it manifests (e.g., "he grows quiet and avoids eye contact, picking at the loose threads on his sleeve").
- Weak or Inconsistent Example Dialogue: This is the big one. Your AI learns more from watching what you do (in the examples) than what you say (in the descriptions). If your dialogue examples don't perfectly match the personality you've laid out, you're sending mixed signals. Make sure every line of dialogue is a masterclass in who your character is.
A wobbly foundation will always lead to a shaky performance. If your AI is ignoring your rules, start by checking these three areas. A solid set of character AI rules is the only way to build a truly immersive and consistent companion.
Ready to put these principles into practice and build your own unforgettable AI companion? On Luvr AI, you have the tools to design incredibly detailed characters from the ground up. Craft their backstory, define their personality, and teach them to talk with precision. Start creating your perfect AI on Luvr AI today!