Create Your Own AI Girlfriend 😈
Chat with AI Luvr's today or make your own! Receive images, audio messages, and much more! 🔥
4.5 stars

Ever had a conversation where you just knew the other person wasn't really listening? They heard your words, sure, but they missed the sigh, the slump in your shoulders, or the flicker of excitement in your eyes. That gap between hearing and truly understanding is what affective computing—also called emotion AI—is designed to bridge for our technology.
In simple terms, affective computing is the science of teaching machines to recognize, interpret, and even simulate human emotions. It gives devices the ability to sense a user's feelings—like joy, frustration, or surprise—by analyzing data from their face, voice, and even physiological signals. It’s all about giving technology a dose of emotional intelligence.

Teaching Technology to Understand You
Imagine talking to a digital assistant that doesn't just hear your words but also catches the hint of frustration in your voice when a task goes wrong. Or picture a gaming character that notices your grin and genuinely celebrates a big win right alongside you. This is the core promise of affective computing.
It’s a move away from the cold, robotic command-and-response interactions we’ve grown used to. Instead of just processing what you say, emotion AI aims to understand how you feel, paving the way for a much richer and more intuitive connection between us and our devices.
Where Did Emotion AI Come From?
The idea of building emotionally aware technology isn't brand new. It was formalized as an academic discipline back in the mid-1990s when MIT professor Rosalind Picard coined the term in her groundbreaking 1997 paper, Affective Computing. Her work laid the foundation for "computing that relates to, arises from, or deliberately influences emotions," marking a huge shift in how we think about the intersection of feelings and machine intelligence. For a deeper dive, you can learn more about the foundations of affective computing directly from her pioneering research.
The entire field is built on a simple but profound premise: for technology to be truly helpful, it must be able to navigate our messy, wonderful, human emotional world.
Affective computing isn't about replacing human connection. It's about augmenting our digital experiences with a layer of emotional understanding, making them more natural, supportive, and effective.
At its heart, affective computing rests on four key abilities that mirror how humans process emotions. Think of them as the building blocks for creating emotionally intelligent AI.
The Four Pillars of Affective Computing
| Pillar | What It Means | Real-World Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Recognizing Emotion | The AI identifies emotional cues from data like facial expressions, voice tone, or heart rate. | Noticing a friend's smile and realizing they're happy. |
| Interpreting Emotion | The system analyzes the recognized cues within a specific context to understand the likely emotion. | Seeing a friend smile at a party and concluding they're having a good time. |
| Simulating Emotion | The AI generates responses (like text, speech, or avatars) that appear to express emotion. | Responding to your friend's smile with a warm, "I'm so glad you're here!" |
| Responding to Emotion | The system takes action based on the user's emotion, adapting its behavior to be more helpful or empathetic. | Seeing your friend looks stressed and offering to help, instead of talking about your own day. |
These four pillars work together to create a feedback loop, allowing technology to move beyond simple logic and engage with us on a much more human level.
So, Why Does It Matter Now?
Our lives are saturated with digital interactions, and the quality of those exchanges is more important than ever. Emotion AI is the key to unlocking a better user experience. It’s what separates a generic, script-following chatbot from a truly supportive AI companion, like the ones you might find on platforms such as Luvr AI.
By understanding our emotions, developers can build systems that are:
- More Engaging: Technology that adapts to your mood can create far more immersive and personalized experiences, from gaming to learning.
- More Supportive: An AI that detects stress or confusion can offer help, encouragement, or just a moment of digital comfort.
- More Intuitive: Instead of waiting for explicit commands, systems can anticipate what you need simply by reading your emotional cues.
How AI Learns to Read the Room
So, how exactly does a machine learn to tell the difference between a sigh of relief and a frustrated groan? It’s not magic. It’s a sophisticated process of pattern recognition, much like how a child learns to connect a parent's tone of voice with their mood. Affective computing systems are trained on massive datasets, teaching them to link specific signals to human feelings.
One of the biggest lessons we've learned in this field is that there’s no single "tell" for emotion. A smile doesn't always mean happiness, and a loud voice isn't always anger. The most reliable systems have to be detectives, gathering clues from multiple channels over time to make an educated guess about how someone truly feels.
The Face as an Emotional Canvas
The most obvious place to start is with the face. Facial expression analysis is a cornerstone of affective computing. An AI is fed millions of images and videos of faces, each one carefully labeled with an emotion—joy, surprise, anger, sadness. Slowly but surely, the model learns to spot the tiny muscular movements and "micro-expressions" tied to each feeling.
It’s a bit like an artist learning to draw portraits. At first, they just draw a generic smile. But with experience, they see the subtle crinkle around the eyes that separates a genuine, heartfelt grin from a polite, social one. The AI learns the same way, pinpointing minute shifts in the eyebrows, mouth, and cheeks to build a far more detailed picture of a person's inner state.
Listening Beyond the Words
Of course, emotion isn't just visible; it's audible. That's where vocal analysis comes in. The words we choose are just one layer of communication. How we say them often tells the real story. An AI can break down an audio clip to analyze its core acoustic features:
- Pitch: A higher pitch can signal excitement or stress.
- Volume: Increased loudness might mean anger, but it could also mean pure joy.
- Tempo: Are you speaking a mile a minute? That could be nerves. A slower pace might suggest sadness or deep thought.
The AI learns to hear the difference between the bright, rising tone of someone sharing good news and the flat, monotone delivery of someone feeling defeated. It’s the digital version of a friend hearing you say, "I'm fine," and knowing instantly that you're anything but.
Reading the Signals We Don't Realize We're Sending
Beyond our faces and voices, AI can also interpret our written words and even our body's unconscious reactions. Text-based sentiment analysis is what allows AI companions and chatbots to grasp the emotional tone of a message. This is absolutely critical for creating interactions that feel real, a topic we dive into in our guides on AI chatbots.
Affective computing isn't about isolating one cue, like a smile or a frown. It's about synthesis—weaving together facial data, vocal tone, written text, and even biological signals to build a holistic and nuanced picture of a person's emotional journey.
Finally, some of the most advanced systems look at physiological signals. They can track things like heart rate, skin conductivity (how much you're sweating), and body temperature. Imagine a video game that notices your heart rate spike during a tense boss battle. That data point, combined with other cues, confirms to the AI that you're feeling stressed or excited. By pulling all these different threads together, the AI can paint a surprisingly accurate and dynamic portrait of human emotion.
Building Empathetic AI From Data to Digital Friend
How does an AI go from processing commands to actually showing something that feels like empathy? It needs a teacher. And in the world of affective computing, that teacher is data—massive, diverse, and deeply human.
We learn to understand each other through a lifetime of social cues and interactions. An AI has to learn in a similar way, but by studying vast "emotional libraries" instead. Think of these not as sterile databases, but as rich textbooks from which an AI studies the subtle flicker of disappointment in a person's eyes or the bright energy of surprise in their voice. This training is the very foundation of its emotional intelligence.
The Power of Emotional Datasets
An AI can’t feel joy, but it can learn to spot the tell-tale patterns associated with it. That’s where high-quality emotional datasets come in. They are curated collections packed with labeled examples of facial expressions, voice recordings, text conversations, and even physiological signals like heart rate. Each entry is a tiny lesson in what it means to be human.
Take the DAIC-WOZ dataset, for example. It’s a collection of over 140 clinical interviews, providing incredibly rich, multimodal data that helps AI models recognize signs of distress. Though originally built to help detect depression, its detailed protocols have made it a gold standard for building more perceptive systems across the board.
The authenticity of an AI companion isn't programmed; it's learned. Its ability to offer a comforting word or share in your excitement is a direct reflection of the quality and diversity of the emotional data it was trained on.
The process is all about bringing different signals together for a more complete picture.
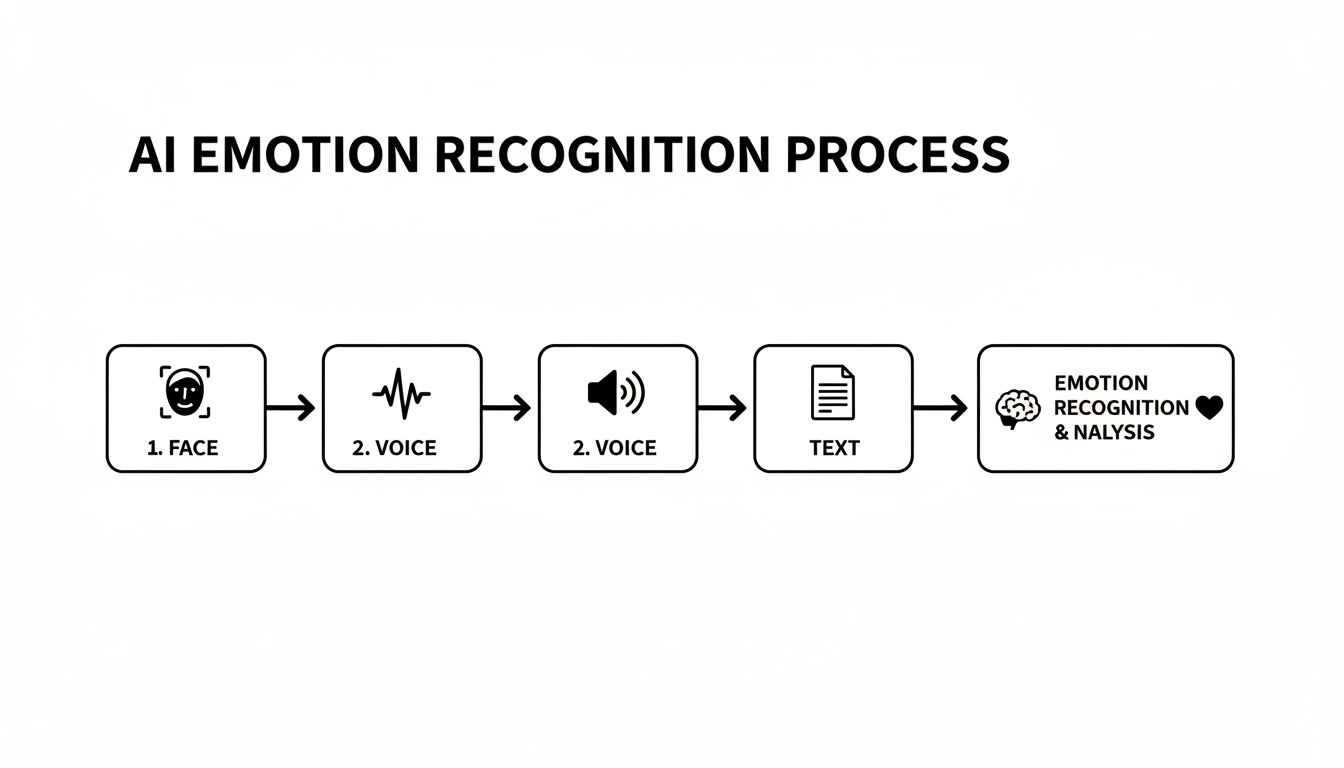
This flowchart really shows how an AI combines cues from faces, voices, and text to build a holistic understanding of someone's emotional state. Relying on just one signal would be like trying to understand a conversation with one ear plugged—you'd miss a lot. This multi-layered approach is what makes it so much more accurate.
From Data to Digital Friendship
Ultimately, all this intensive training has one simple goal: to create more meaningful, human-centric interactions. The whole point is to build an AI that doesn’t just respond, but genuinely relates.
When a system learns to pick up on these nuanced emotional cues, it can adapt its behavior on the fly. This is exactly what allows a digital friend to offer a supportive message when you’re feeling down or celebrate a big win with you. This deep, learned empathy is fundamental to the experience of an AI character chat, transforming what could be a simple program into a truly responsive companion. It’s a process that ensures every conversation feels personal, dynamic, and genuinely understanding.
Affective Computing in Your Daily Life
You might think of emotion-sensing AI as something out of a sci-fi movie, but the truth is, affective computing is already here. It's quietly shaping our daily interactions with technology, making our devices less like tools and more like partners. While the field is still growing, its applications are already starting to change what we expect from the digital world.

This isn't some abstract concept; it's powering real systems that make a difference. In healthcare, for instance, it's used to build monitors that can pick up on subtle signs of a patient's pain or distress, giving caregivers a heads-up when someone needs help. In education, it's the magic behind learning software that can tell when a student is getting frustrated or bored, then adjust the lesson on the fly to keep them locked in.
What these examples show is a huge shift in thinking. We’re moving away from a world where we have to learn the quirks of rigid software. Instead, the software is learning to adapt to us—to our moods and feelings—creating a much more helpful and human experience.
From Chatbots to True Companions
Nowhere is this more apparent than in the world of conversational and companion AI. This is where affective computing really comes to life, turning a clunky chatbot into something that feels like a real friend or confidant. It's the secret sauce that gives these companions emotional depth and makes the relationship feel real.
An AI companion built with emotion AI doesn't just hear your words; it feels the meaning behind them.
- Emotional Memory: It remembers how you were feeling. If you mentioned being anxious about a big meeting, it might check in a few days later to see how things went. It's a simple act of digital thoughtfulness.
- Contextual Reactions: You share great news, and instead of a canned "Congratulations," it responds with genuine excitement, using upbeat language and emojis that match your own energy.
- Empathetic Support: When you're having a rough day, it can detect sadness or frustration in your voice and text, offering words of comfort and support. It becomes a judgment-free zone to just be yourself.
This is what builds the connection. It’s the AI’s ability to react with emotional intelligence that makes the bond feel genuine.
Affective computing is what allows an AI to graduate from a simple tool to a source of comfort, celebration, and connection. It’s what makes our digital interactions feel less robotic and more human.
Creating Deeper, Meaningful Experiences
When an AI can understand and react to human emotion, developers can build experiences that are just so much more engaging. An AI character can celebrate your wins, offer a digital shoulder to lean on when you're down, and remember the small things that make you, you.
This isn't about feeding an AI a script. It's about giving it the ability to learn your emotional tells and adjust its own behavior to connect with you on a deeper level. This is the core idea that lets a platform like Luvr AI create characters that feel alive, offering not just small talk but real companionship.
In the end, it all leads to a user experience that is richer, more memorable, and profoundly more meaningful.
The Ethical Maze of Emotion AI
While the promise of emotionally intelligent tech is huge, this kind of power brings with it some serious responsibility. The field of affective computing isn't just a technical puzzle; it's an ethical maze that demands we watch our step. If we get it wrong, emotion AI could amplify biases, trample on privacy, and be used to manipulate people. But if we approach it with care, it can genuinely be a force for good.
The first big roadblock is cultural nuance. Emotions simply aren't universal. A gesture of respect in one culture can be deeply offensive in another, and a smile can mean a dozen different things depending on the situation. If an AI is trained mostly on data from one group of people, it’s guaranteed to misread the emotional expressions of everyone else.
This feeds directly into the danger of algorithmic bias. An AI model is only as good as the data it’s fed. When training datasets don't include a diverse mix of people, the system will inevitably make flawed, or even harmful, judgments about the emotional states of underrepresented groups.
Privacy and Protecting Emotional Data
Maybe the most urgent issue of all is privacy. Your emotional data—the tiny inflections in your voice, the micro-expressions that flash across your face—is profoundly personal. It’s like a digital fingerprint of your inner world. Who gets to see that data, and what they do with it, is one of the most critical ethical questions we face in technology today.
Protecting user privacy isn't just a nice-to-have feature; it's the absolute, non-negotiable foundation of trustworthy affective computing. People need to have complete confidence that their emotional data is secure, kept confidential, and only used in ways they've clearly agreed to.
Building that trust requires a serious commitment to responsible innovation. It means designing systems with privacy baked in from the very beginning, not bolted on as an afterthought. This comes down to a few key practices:
- Robust Encryption: Making sure all data is unreadable to anyone who shouldn't see it, both when it's being sent and when it's being stored.
- Data Anonymization: Stripping away any personal identifiers from emotional data so it can’t be linked back to a specific person.
- Explicit Consent: Giving users straightforward, easy-to-understand information about what data is being collected and getting their clear permission first.
A Commitment to Responsible AI
Getting through these challenges takes transparency and a user-first mindset. The goal isn't just to build powerful AI. It's to build technology that is fundamentally safe, fair, and respectful to the people it's designed to help. It’s all about building trust, one interaction at a time. This dedication to responsible development has to be a core principle for any platform in this space.
For anyone who wants to go deeper on these issues, you can find more insights into the complex world of AI ethics in our dedicated articles.
Ultimately, the entire future of affective computing hinges on getting this right. We have to make sure that as our technology gets better at understanding emotions, it also becomes more ethically grounded. That's how we create a future where our digital interactions aren't just smarter, but truly safer for everyone.
Where Emotionally Intelligent Technology is Headed Next

We’ve walked through the ins and outs of affective computing, from its roots in emotion recognition to the real-world tools it powers today. At its core, this is all about teaching machines to recognize, understand, and even adapt to human feelings. The result is a richer, more intuitive, and frankly, more human way of interacting with technology.
But what's next? If you look toward the horizon, it’s clear we're just scratching the surface. The true potential of emotionally intelligent systems is only now beginning to take shape, promising a future where our devices feel less like tools and more like genuine partners.
A World That Finally Gets Us
Let's get practical for a moment. Imagine a mental wellness app that doesn't just ask you to log your mood. Instead, it senses the subtle shifts in your voice or typing patterns that signal rising stress, then gently nudges you with a breathing exercise right when you need it most.
Or think about creative software that knows when you've hit that elusive "flow state." It could automatically silence notifications and pare back the interface, creating a digital bubble to protect your focus. We could see educational platforms that adapt not just to what a student knows, but to their level of curiosity, their moments of frustration, or that "aha!" spark of understanding.
This isn't science fiction. It’s the driving force behind a global affective computing market expected to skyrocket to over $180 billion by 2026. People want technology that works with them, not just for them.
The ultimate goal of affective computing is not to replace human connection, but to augment it. It aims to build a world where our technology is a more empathetic, supportive, and understanding partner in our lives.
The point isn't to create machines that have feelings. The real win is building technology that truly understands ours. Whether it’s an AI companion from a platform like Luvr AI that learns your personality or a system that helps you be more creative, the future of tech is emotionally aware.
By finally closing the gap between human emotion and machine logic, affective computing is setting the stage for an entirely new kind of technology. One that isn't just smarter, but wiser, kinder, and more in tune with what it means to be human.
Your Questions About Affective Computing, Answered
Alright, so we've covered the what and the how of affective computing. But you probably still have some questions buzzing around. Let's dig into some of the most common ones.
Is Affective Computing Just a Fancy Name for Sentiment Analysis?
That’s a great question, and the answer is no—though they are definitely cousins.
Think of sentiment analysis as a simple thumbs-up or thumbs-down. It’s great at looking at a block of text and telling you if the general vibe is positive, negative, or neutral. It’s useful, but it’s a pretty broad measurement.
Affective computing, on the other hand, is like having a full-blown emotional radar. It’s not just looking for "good" or "bad." It’s trying to identify specific, nuanced emotions—joy, surprise, frustration, sadness—by pulling from way more than just text. It’s analyzing vocal tone, facial cues, and sometimes even biometric data to get a much richer, more detailed picture of how someone is actually feeling.
Simply put, sentiment analysis gauges opinion, while affective computing tries to understand the full spectrum of human emotion.
How Does an AI Companion Actually Use This Stuff?
This is where it gets really interesting. For an AI companion, affective computing is the secret sauce that makes the conversation feel real and, well, human. The AI is constantly listening—not just to your words, but how you say them.
It analyzes your language, phrasing, and word choices to get a read on your emotional state. From there, it adjusts its own responses to match your mood.
For instance, if you share some fantastic news, it can pick up on that excitement and reply with an equally enthusiastic tone. If you're venting about a rough day, it knows to dial it back and offer support and comfort. This is what allows an AI companion to build a genuine rapport with you, creating a connection that feels meaningful.
What About Privacy? Isn't This a Little Creepy?
The privacy question is a big one, and it's absolutely crucial. We're talking about incredibly personal data here—your emotions. The biggest concern is how this data is collected, used, and protected.
Any company worth its salt in this space has to be completely transparent about what information it’s gathering and how it's being kept safe. You should expect, and demand, a few non-negotiables:
- Rock-Solid Encryption: Your data should be scrambled and unreadable to anyone who isn't authorized to see it.
- No-Nonsense Data Policies: You should be able to easily understand what's collected and why.
- You're in Control: Nothing should be collected without your explicit consent.
These aren't just nice-to-haves; they are fundamental safeguards to ensure your emotional data stays private and secure.
Ready to see what an emotionally intelligent AI feels like? You can find characters who actually listen, understand, and connect with you on a much deeper level. Find your perfect AI companion with Luvr AI today at https://www.luvr.ai.