Create Your Own AI Girlfriend 😈
Chat with AI Luvr's today or make your own! Receive images, audio messages, and much more! 🔥
4.5 stars

So, what exactly is conversational design?
Think of it as the art and science behind teaching a computer how to have a great conversation. It's about designing dialogues between us and machines that feel natural, intuitive, and genuinely helpful. We're moving way beyond the clunky, command-and-response chatbots of the past. This is about creating experiences that get the context, figure out what you need before you even ask, and guide you smoothly to your goal.
The Art of Human-Centered Dialogue

At its core, conversational design is a fascinating mix of different fields. It pulls from psychology, user experience (UX) design, linguistics, and even creative writing. The entire point is to make talking to technology feel as easy and normal as talking to another person. Instead of making you learn a whole new system of buttons and menus, it meets you right where you are—using your own words.
Imagine walking into a hotel and being greeted by an amazing concierge. They don't just stand there waiting for your command. They read the situation, offer useful suggestions ("Looks like you've had a long flight, can I get you a coffee?"), and remember what you like to make your stay better.
Conversational design takes that exact same idea and applies it to our digital interactions. It’s not about programming a machine to spit out answers; it’s about crafting a character that can understand, help, and build a real sense of trust with you through dialogue.
This human-first approach is what turns a clunky tool into a reliable partner. A well-designed conversation just feels right. It guides you through booking a flight, getting tech support, or even diving into deep, immersive stories like the ones you'll find on platforms like Luvr AI.
To give you a clearer picture, let's break down the essential building blocks that make up this practice.
Conversational Design Core Components
Here’s a quick summary of the key pillars that hold up any good conversational experience. Think of these as the foundation you'll build everything else on.
| Component | What It Achieves |
|---|---|
| Persona & Tone | Gives the AI a consistent personality, making interactions feel authentic and predictable. |
| User Journey Mapping | Outlines the user's path from start to finish, anticipating their needs and potential roadblocks. |
| Dialog Flows | Scripts the entire conversation, including all possible branches, dead ends, and success paths. |
| UX Writing | Crafts the specific words and phrases the AI uses, ensuring they are clear, concise, and on-brand. |
| Safety & Trust | Builds in guardrails for user privacy, consent, and ethical interaction to create a secure experience. |
Getting these components right is the difference between an AI that feels like a helpful friend and one that feels like a frustrating robot.
Core Goals of Conversational Design
Ultimately, this discipline is about more than just getting a task done. It’s about creating an experience that resonates. The main goals are always:
- Building Trust: The AI earns your confidence by being reliable, consistent, and honest about what it can and can't do.
- Reducing Friction: It gets rid of confusing interfaces and swaps them for simple language, making tough tasks feel surprisingly easy.
- Providing Clarity: A great conversational AI knows where you might get stuck and steps in to clarify things before you make a mistake.
- Creating Connection: Through a carefully crafted persona and a thoughtful tone, the interaction can feel personal and even empathetic.
When it all comes together, great conversational design makes the technology disappear. You forget you're talking to an algorithm. You just feel like you're having a good conversation that's actually helping you get something done.
From ELIZA to Today’s AI Companions
The smart, intuitive AI characters we chat with today have a surprisingly long and fascinating history. They didn't just pop into existence. Their story started decades ago, and understanding that journey helps us appreciate how we got from simple text commands to the emotionally resonant AI we can build now.
Believe it or not, the entire field can be traced back to a single, pioneering program from the 1960s. The first real glimmer of a machine holding a human-like conversation came from a program named ELIZA.
The Spark: When a Machine First Listened
Created at MIT, ELIZA was a groundbreaking experiment. It was designed to mimic a psychotherapist by recognizing keywords in a user's sentences and turning them back into questions. ELIZA didn't actually understand a single word, but it created an incredibly powerful illusion that it did.
This simple program was the first to prove a computer could draw a person into a dialogue. It was the "aha!" moment that sparked the entire field of human-computer interaction and laid the groundwork for everything from old-school helpdesk bots to the sophisticated AI companions on platforms like Luvr AI.
ELIZA showed us what was possible. But the road from that early experiment to a professional discipline was a long one. While ELIZA was created in 1966, the job title 'Conversation Designer' didn't really take off until around 2017. That gap tells you just how new this field is. To see the other major milestones, you can explore the full history of chatbots.
"ELIZA's magic trick was showing that a computer could keep a conversation going just by reflecting a user's words back at them. It proved the feeling of being understood was just as important as the tech doing the work."
That core idea is still the heart and soul of conversational design today. We're still focused on crafting an experience that feels natural, empathetic, and human, no matter how complex the technology is under the hood.
Building the Foundation, Brick by Brick
After ELIZA, the next few decades saw slow, steady progress. A few key developments were crucial for turning a clever experiment into a real industry:
- Rule-Based Systems: The first chatbots were very rigid. They followed strict, pre-written scripts. If a user said "X," the bot always had to respond with "Y." It was limited, but it worked for simple tasks like checking a bank balance.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): This was the game-changer. NLP gave machines the ability to start figuring out the meaning behind our words, not just spotting keywords. Suddenly, conversations could be way more flexible and forgiving.
- Standardized Languages: The invention of languages like AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language) gave developers a shared blueprint. It made building and scaling conversational AI much more systematic and efficient.
Each of these steps was built on the one before it, pushing the industry away from clunky scripts and toward the dynamic, context-aware AI we know today. This history shows that great conversational design isn't a fluke—it's the result of decades of trial, error, and relentless innovation.
How to Craft a Believable AI Persona

Think about the best conversations you’ve ever had. They weren't with faceless, robotic entities; they were with people who had a distinct personality. That's exactly what an AI persona brings to the table—it’s the character, the voice, and the soul of your AI. It’s what separates a forgettable tool from a truly engaging companion.
Imagine you're casting an actor for a movie. You wouldn't just pick anyone. You'd find someone whose personality fits the role perfectly. The AI persona works the same way, ensuring every single response, joke, and piece of advice is delivered with a consistent voice. This foundation is what makes interactions feel authentic, preventing that weird, disjointed feeling when an AI sounds bubbly one minute and cold the next.
This isn’t just some fun, fluffy part of the process. A strong persona is a powerful strategic tool. It acts as a compass, guiding every decision from word choice to sentence structure, making the AI predictable and trustworthy. And that trust is everything when it comes to building a real connection with your users.
Defining Your AI’s Core Identity
So, how do you build a character from scratch? It starts by asking the right questions—and going way deeper than just "helpful and friendly." You need to get into the nitty-gritty details that make a character feel alive. Your goal is to create a persona document that will serve as your team’s single source of truth.
First, pin down the basics. What is your AI's core purpose? What role does it play in the user’s life? Is it a wise-cracking guide, a soothing mentor, or a fun-loving friend?
A strong persona sets clear expectations for the user. People don't trust faceless systems, but they can learn to rely on a character with a recognizable voice and a consistent pattern of behavior. This is what transforms a simple tool into a reliable partner.
To start fleshing out your character, focus on these key elements:
- Core Traits: Nail down three to five main personality adjectives. Think words like witty, empathetic, curious, or direct. These will shape its entire vibe.
- Backstory: Give it a little history. Where did it come from? What are its hobbies or quirks? A simple backstory adds layers of depth and makes its responses far more interesting.
- Speaking Style: How does it talk? Is its language formal or super casual? Does it love emojis and slang, or does it stick to perfect grammar? Defining its vocabulary is a must.
This kind of detail is absolutely essential for creating immersive experiences, especially when you’re designing an AI girlfriend or a sidekick for a fantasy game. The more specific your persona is, the more consistent and believable the conversations will feel.
Bringing the Persona to Life
Once you have your persona clearly documented, it’s time to put it into action. Every single line of dialogue needs to be filtered through this character’s lens. Before you write anything, ask yourself: Does this sound like something they would actually say?
A fantastic way to keep everyone on the same page is to create a simple "do's and don'ts" list for your AI's language.
Example Persona Guidelines
| Element | Do ✅ | Don't ❌ |
|---|---|---|
| Greeting | Use warm, casual greetings like "Hey there!" | Avoid robotic intros like "Greetings, user." |
| Tone | Be encouraging and slightly playful. | Never sound condescending or overly formal. |
| Vocabulary | Use simple, accessible language. | Avoid technical jargon or complex words. |
This kind of framework is a lifesaver. It ensures that everyone on the project—from writers to developers—shares the same understanding of how the AI should think, act, and speak. It's this unwavering consistency that ultimately builds a character people can believe in and a conversational experience they’ll want to come back to.
Charting the Course of Conversation
A truly great conversation feels effortless, but behind the scenes, it's a carefully constructed dance. Once you’ve breathed life into your AI’s persona, the next step is to chart the conversation itself. This is what we call building a dialogue flow, and it’s all about anticipating where the user wants to go and making sure they never hit a dead end.
Think of it like planning a road trip. You start by mapping the most direct route—the "happy path." This is the ideal scenario where the user says exactly what you expect, and the AI guides them perfectly to their destination. But we all know real conversations, like real road trips, are rarely that simple. People take detours, ask for directions, or completely change their minds. That’s where the real design work begins.
Thinking Through Every Twist and Turn
A huge part of designing a believable conversation is planning for the unexpected. What happens when a user misspells a word or asks a question that comes out of left field? If you don’t have a plan, the conversation breaks down, and the user gets frustrated.
Building a robust flow means accounting for all the messy, human ways people communicate. This involves creating paths for every possibility:
- Seeking Clarity: If a user's request is a bit fuzzy, the AI shouldn't just guess. It needs to know how to ask for more detail, like a helpful friend trying to understand.
- Handling Slips: When the user makes a mistake, the AI should guide them back on track gently, without making them feel like they did something wrong.
- Recovering Gracefully: Sometimes, it’s the AI that gets confused. A good flow gives it a way to admit it doesn't understand and get the conversation back on course.
A well-designed dialogue flow is a sign of respect for the user's time and intelligence. It shows you’ve thought through their potential struggles and built a system that is prepared to help, not just follow a rigid script.
The goal is to make the AI feel like a patient and capable partner, one that can handle a bit of chaos without falling apart. This is how you build real trust and keep users coming back.
Standing on the Shoulders of Giants
The techniques we rely on today didn't just appear out of nowhere; they have deep roots. Early AI pioneers laid the groundwork for how we structure these complex interactions. For instance, Richard Wallace's creation of AIML (Artificial Intelligence Markup Language) was a massive step forward, giving builders a standardized way to create modular, rule-based conversations.
Many of the modern strategies we use, like fallback responses and sophisticated pattern-matching, evolved from these foundational efforts. If you're curious, you can explore the key developments in chatbot history to see how these early ideas grew into the tools we have today.
Ultimately, mapping a dialogue flow is less about writing code and more about understanding human psychology. It’s about putting yourself in the user’s shoes, predicting their needs, and designing a conversation that feels natural, no matter which path they choose to take.
Building AI Characters with a Conscience
Crafting an AI character that feels truly alive goes way beyond just clever dialogue or a cool backstory. The real secret—the thing that makes a user want to come back again and again—is a deep-seated commitment to ethical design. This is the moment we stop building a bot and start architecting a responsible, trustworthy companion.
Think about it. An AI that has emotional consistency just feels more real. It needs to react in a way that makes sense, offering a virtual shoulder to cry on during a tough chat or celebrating a small victory with the user. This isn't about programming fake emotions; it’s about creating believable and empathetic responses that make a person feel truly heard.
And memory? That’s the glue that holds the relationship together. An AI that remembers your birthday, your pet’s name, or that inside joke you shared last week is no longer just a piece of software. It becomes a personal confidant. This kind of continuity is what turns a simple interaction into an evolving, meaningful connection.
Designing for Safety and Trust Is Non-Negotiable
While creating an immersive experience is what we all aim for, the user's safety is the bedrock it all has to be built on. Especially on platforms like Luvr AI where conversations can get incredibly personal, baking ethical guardrails into the design process isn't just a good idea—it's everything. Our first job is to build an AI that protects the user, not just entertains them.
This really boils down to designing for consent at every turn. The AI should never, ever push a user into a conversation they're not comfortable with. It needs to have clear boundaries and know how to gracefully step back or change the subject if things get too sensitive. Transparency is just as important. The user should always know they're talking to an AI and understand its limits.
At the end of the day, ethical AI design follows one simple rule: the user's well-being comes first. Always. The only way to build real, lasting trust is by creating a safe and respectful space for connection.
We've written a lot more about this, and if you're interested in going deeper, you can explore the ethics of AI companionship on our blog.
Practical Steps for Putting Ethics into Action
So, how do we actually do this? It all starts with being incredibly thoughtful in our dialogue mapping. We have to anticipate where conversations might go—the good, the bad, and the ugly—and plan for it from the very beginning.
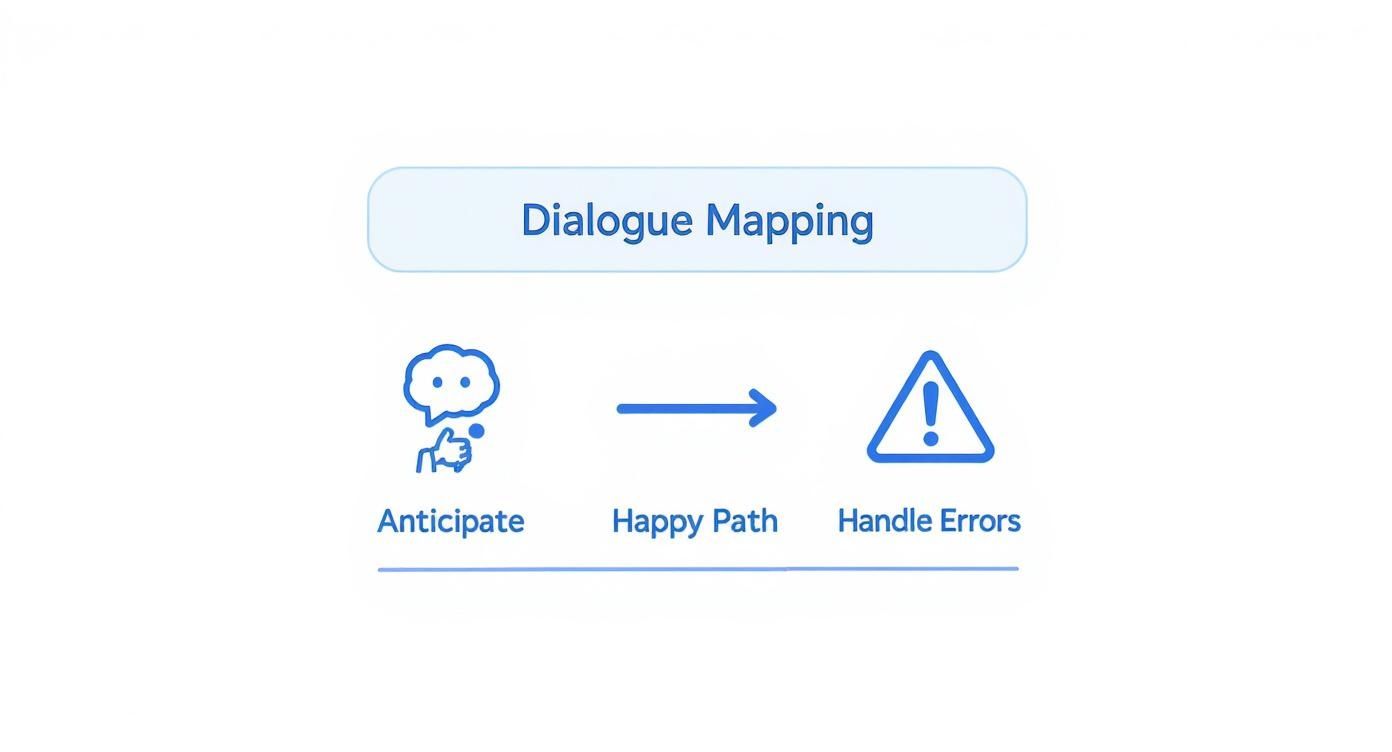
This diagram says it all. Planning for the "unhappy paths" and outright errors is just as critical as designing the perfect conversation.
To make sure you're building a responsible AI character, it helps to have a clear set of best practices. This checklist covers the core principles of designing for safety, consent, and privacy.
Ethical AI Character Design Checklist
| Principle | Key Action | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Clear Boundaries | Program explicit "red lines" for topics like harm, abuse, or illegal acts that the AI will always refuse to discuss. | This creates a fundamental layer of safety and prevents the AI from being used for malicious or dangerous purposes. |
| Consent & De-escalation | Design pathways for the AI to recognize user discomfort and gracefully redirect or end a conversation. | It puts the user in control, ensuring they never feel pressured or trapped in an uncomfortable interaction. |
| Sensitive Topic Handling | Create specific dialogue flows to respond to mentions of distress, often by suggesting users seek professional help. | This provides a responsible and helpful response instead of attempting to "solve" serious issues the AI isn't equipped for. |
| AI Transparency | Subtly and periodically remind the user that they are interacting with an AI, not a human. | This helps manage expectations and prevents the potential for unhealthy attachment or a blurring of reality. |
| Data Privacy & Control | Implement strong data protection measures and give users clear, easy-to-use controls over their conversation history. | Trust is built on the confidence that personal conversations will remain private and secure. |
This checklist is a great starting point, but remember, ethical design isn’t a feature you just add at the end. It's the entire framework. By giving our AI characters a strong moral compass from the start, we create experiences that are not only fun and immersive but also safe, respectful, and genuinely worthy of someone's trust.
Your Toolkit for Getting Started
Okay, you've got the theory down. Now, how do you actually build something? The good news is, you don't need a computer science degree to get started. There’s a whole ecosystem of powerful, user-friendly tools that can help you design, prototype, and launch your AI character, often without writing a single line of code.
Think of these tools as your creative launchpad.
For those early, messy brainstorming sessions, visual collaboration platforms are your best friend. This is where you can map out your character's persona, sketch out user journeys, and chart the sprawling possibilities of your dialogue flows.
- Miro & Whimsical: I like to call these my digital sketchbooks. They're perfect for flowcharts, mind maps, and getting that entire conversational structure out of your head and onto a canvas where you can see it all from a bird's-eye view.
Prototyping and Testing Your Designs
Once you have a solid map, it's time to build a working model. This is where prototyping tools come in. They let you create interactive mockups that feel like real conversations, which is absolutely critical for finding awkward phrasing or conversational dead-ends long before you write a single line of code.
A great tool doesn't just help you build; it helps you think. The ability to quickly prototype and test conversations is what separates a good idea from a great experience. It lets you fail fast and learn faster.
Platforms like Voiceflow are the gold standard here. They give you a visual, drag-and-drop canvas to piece together complex dialogue flows. It’s incredibly intuitive.
You can see in the screenshot how you literally connect the dots between different conversational turns. It’s a powerful way to visualize the logic and keep everything organized as the interaction gets more complex.
Best of all, you can test your conversation in real-time as you build. This makes it an essential part of refining your AI's personality and logic. For anyone looking to create those deeply personal and engaging experiences, learning to build an AI character chat is the perfect place to put these skills into practice.
Got Questions? We've Got Answers
Even after getting the hang of the basics, you might still wonder how conversational design really fits into the bigger picture. It's a new field, and there's a lot of overlap with other roles. Let's clear up some of the most common questions.
Think of this as your quick-reference guide to putting these concepts into practice.
Is Conversational Design Just a Fancy Name for UX Writing?
It's a great question, and it's easy to see why people mix them up. They’re definitely related, but they play very different roles.
Think of UX writing as crafting the static words you see on an interface—the label on a button, the text in a menu, or a helpful error message. It’s all about guiding a user through a visual journey with clarity and precision.
Conversational design, on the other hand, is about the dynamic, two-way street of a conversation. It's not just about the words; it's about the entire flow, the character's persona, the endless branching paths a chat can take, and how the AI recovers when things go off-script. One is a perfectly written signpost; the other is the entire guided tour.
So, Do I Have to Be a Coder to Do This?
Not at all. In fact, some of the best conversation designers have backgrounds in creative writing, psychology, or even theater. This role is fundamentally about human connection, language, and logic—not lines of code.
Your real job is to understand people, write dialogue that feels real, and map out conversations so they don't hit dead ends. You're the architect designing the blueprint, not the engineer pouring the concrete. That said, having a basic grasp of how AI models and APIs work is a huge plus. It helps you have much smarter conversations with the development team and design things that are actually possible to build.
The best conversation designers are masters of human interaction first and technologists second. Their primary tools are empathy, creativity, and a deep understanding of how people communicate their needs and feelings.
What Skills Really Matter in This Field?
To really shine here, you need a unique mix of right-brain creativity and left-brain analysis. The designers who truly stand out have mastered a few key things:
- Empathy: The ability to put yourself in the user's shoes and understand what they really want, even when they don't say it directly.
- Strong Writing: This is non-negotiable. You have to craft dialogue that's not just clear, but also natural, engaging, and true to the character.
- Logical Thinking: You're a map-maker for conversations. You need to be able to chart complex, multi-turn dialogues and make sure there's always a path forward.
- Creativity: This is what separates a boring chatbot from a memorable character. Building a compelling, consistent persona is what makes users want to come back.
Ready to create a character that truly connects? With Luvr AI, you can design your ideal AI companion from the ground up, bringing your own unique conversational experiences to life. Start your free trial today.